JSP详解
一、什么是JSP
Java Server Pages:Java服务端页面,也和Servlet一样开发动态web
写JSP就像在写HTML
区别:
HTML只给用户提供静态数据
JSP页面中可以嵌入JAVA代码,为用户提供动态数据;
二、JSP原理
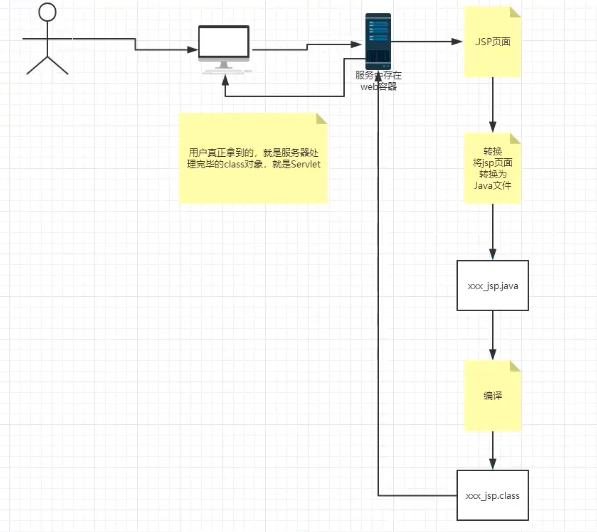
思路:JSP到底是如何执行的?
代码层面没有任何问题
服务器内部工作
tomcat中有个work目录
IDEA中使用Tomcat会在IDEA的tomcat中产生一个work目录
jsp页面或转化为java程序
浏览器向服务器发送请求,不管访问什么资源,其实都在访问Servlet
JSP最终也会被转化为一个Java类!,JSP本质上就是一个Servlet!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public void _jspInit () } public void _jspDestroy () } public void _jspService (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
判断请求
内置了一些对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 final jakarta.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; final jakarta.servlet.ServletContext application;final jakarta.servlet.ServletConfig config;jakarta.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null ; final java.lang.Object page = this ;jakarta.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null ; jakarta.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null ;
输出页面前增加的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8" ); pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this , request, response, null , false , 8192 , true ); _jspx_page_context = pageContext; application = pageContext.getServletContext(); config = pageContext.getServletConfig(); out = pageContext.getOut(); _jspx_out = out;
以上的这些对象,问你可以在JSP页面中直接使用!
在JSP中只要是Java代码就会原封不动的输出;如果是HTML代码,就会被转化为如下格式输出到前端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 out.write("<!DOCTYPE html>\n" ); out.write("<html lang=\"en\">\n" ); out.write(" <head>\n" ); out.write(" <meta charset=\"UTF-8\" />\n" ); out.write(" <title>" ); out.print(request.getServletContext().getServerInfo() ); out.write("</title>\n" ); out.write(" <link href=\"favicon.ico\" rel=\"icon\" type=\"image/x-icon\" />\n" ); out.write(" <link href=\"tomcat.css\" rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" />\n" ); out.write(" </head>\n" );
三、JSP基础语法
任何语言都有自己的语法,JSP作为Java技术的扩充,它拥有一些自己扩充的语法(了解知道即可),Java的所有语法JSP都支持!
1. JSP导包:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > javax.servlet</groupId > <artifactId > servlet-api</artifactId > <version > 2.5</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > javax.servlet.jsp</groupId > <artifactId > javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId > <version > 2.3.3</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > taglibs</groupId > <artifactId > standard</artifactId > <version > 1.1.2</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId > <artifactId > jstl-api</artifactId > <version > 1.2</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
2. JSP表达式
1 2 3 4 5 6 <%--JSP表达式 作用:用来将程序的输出结果,输出到客户端 <%= 变量或表达式%> --%> <%=new java.util.Date()%>
3. JSP脚本片段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <%--脚本片段--%> <% int n=0 ; %> <%--在代码中嵌入HTML元素--%> <% for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { %> <h1>hello</h1> <% } %>
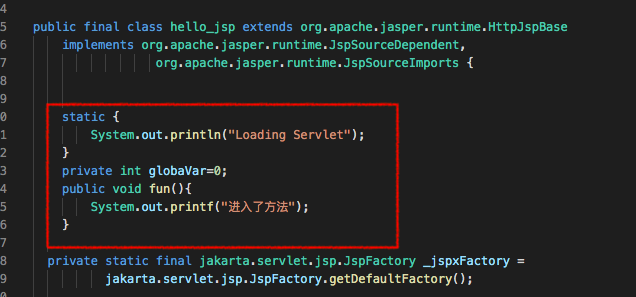
4. JSP声明
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <%! static { System.out.println("Loading Servlet" ); } private int globaVar=0 ; public void fun () System.out.printf("进入了方法" ); } %>
被声明过的语句会被编译到JSP生成的Java的类中,其他的,就会被放在_jspService方法中
JSP的注释不会在客户端显示,HTML的会
四、 JSP指令 (page、include、taglib)
1. page指令
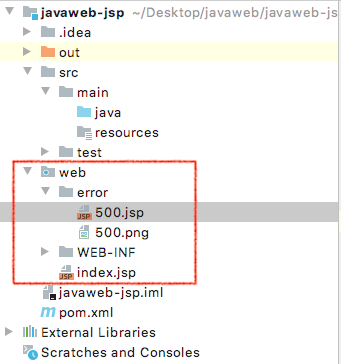
可以用来配置错误页面(erroPage)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <!-- page自定义500 错误 --> <!-- 在index.jsp中写入 --> <%@page errorPage="error/500.jsp" %> <!-- 在500. jsp中写入 --> <body> <!-- JSP获得项目路径 --> <img src=${pageContext.request.contextPath}/error/500. png alt="500" > </body>
配置错误页面方法二 :直接在xml中配置(推荐使用)
1 2 3 4 5 6 <error-page > <error-code > 404</error-code > <location > /error/404.jsp</location > </error-page >
2. include指令
1 2 3 4 5 <body> <%@include file="common/header.jsp" %> <h1>我是主体</h1> <%@include file="common/footer.jsp" %> </body>
拼接页面的第二种方式(jsp:include标签引用)
1 2 3 4 5 <body> <jsp:include page="common/header.jsp" /> <h1>我是主体</h1> <jsp:include page="common/footer.jsp" /> </body>
最终效果注意:include是将header.jsp和footer.jsp的内容拼接到当前页面中。相当于复制粘贴过来。然而,jsp:include标签则是相当于引用
五、JSP内置对象及作用域
九大内置对象
PageContext 存东西
Request 存东西
Response
Session 存东西
Application【ServletContext】 存东西
config【ServletConfig】
out 输出
page
exception
JSP存数据对象的作用域:
PageContext
1 2 3 4 pageContext.setAttribute("name1" ,"倪矗1号" ); request.setAttribute("name2" ,"倪矗2号" ); session.setAttribute("name3" ,"倪矗3号" ); application.setAttribute("name4" ,"倪矗4号" );
修改pageContext对象的作用域
1 2 3 4 5 pageContext.setAttribute("name1" ,"倪矗1号" ,PageContext.SESSION_SCOPE);
使用场景:
request:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了
pageContext实现请求转发:
1 pageContext.forward("/index.jsp" );
六、JSP标签、JSTL表达式、EL表达式
EL表达式: ${}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <form action ="coreif.jsp" method ="get" > <input type ="text" name ="username" value ="${param.usernaem}" > <input type ="submit" value ="登录" > </form >
1. JSP标签:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <!-- 1. 请求转发标签 --> <jsp:forward page="/pageContextDemo01.jsp" > <jsp:param name="name" value="倪矗" /> <jsp:param name="age" value="18" /> </jsp:forward> <!-- 2. 引用文件标签 --> <jsp:include page="common/header.jsp" /> <h1>我是主体</h1> <jsp:include page="common/footer.jsp" /> <!-- 3. 引用实体类(JavaBean)标签 --> <jsp:useBean id="people" (对象) class "com.nichu.People" (类) scope="page" (作用域)/> <!-- 4. 给对象赋值 --> <jsp:setProperty name="people" property="address" value="杭州" /> <jsp:setProperty name="people" property="name" value="倪矗" /> <jsp:setProperty name="people" property="id" value="1" /> <jsp:setProperty name="people" property="age" value="18" /> <!-- 5. 取值 --> <jsp:getProperty name="people" property="name" /> <jsp:getProperty name="people" property="id" /> <jsp:getProperty name="people" property="adress" /> <jsp:getProperty name="people" property="age" />
2. JSTL表达式
JSTL标签库的使用是为了弥补HTML标签的不足;它自定义了许多标签,可以供我们使用,标签库的功能和java代码一样!JSTL标签库
七、JavaBean
实体类
必须要有一个无参构造
属性必须私有化
必须有get、set方法